Introduction to Abortion Laws
Knowing your abortion rights and options has gotten way more complicated than it used to be. Abortion law changed dramatically in 2022 and is continuing to change. With the overturning of Roe v. Wade, abortion is no longer a federally guaranteed right. It is now up to the States and each state has its own abortion laws. Many states have seriously restricted abortion or outlawed it altogether. But abortion is NOT banned nationwide!
Regardless of where you live – whether in a state that allows abortion or in a state that has banned it – you still have options to get a safe, legal abortion if you need it. But you need to understand the laws as they relate to you based on the state where you live so that you know how you will need to go about it.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of abortion law in the United States to help you understand your rights and be better informed about what is and isn’t allowed when it comes to abortion.
“Is abortion legal?”
Today, the answer to this question is it depends where you live. Previous to 2022, Roe v. Wade guaranteed access to abortion care for all women across the United States. But in 2022, the Supreme Court’s landmark decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization overturned Roe v. Wade. This totally changed the legal framework surrounding abortion in the U.S., leading to a patchwork of laws that vary widely from state to state. Understanding these laws is essential to know your specific rights in your state and what options and resources are available – so that you can make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
Understanding Abortion Law in the United States:
A Brief History on How We Got to Where We are Today
The history of abortion law in the United States is a complex tale of changing legal standards and social attitudes. Before the landmark Supreme Court case Roe v. Wade in 1973, abortion was heavily restricted or outright banned in many states. This meant that countless women were forced to seek unsafe and illegal abortions, often risking their lives in the process.

Roe v Wade – Guarantee of Abortion Rights Nationwide
Roe v. Wade was a groundbreaking decision that recognized a woman’s constitutional right to privacy, which extended to her right to choose to have an abortion. This decision effectively legalized abortion nationwide, overriding many state laws that had previously restricted or banned the practice. Roe v. Wade established a trimester framework that allowed states to regulate but not ban abortion during the first trimester, allowed for regulation in the second trimester, and permitted states to ban abortion in the third trimester, except when the mother’s life was at risk.
Some States Begin to Add Restrictions
The decades following Roe v. Wade saw various legal challenges and adjustments, with significant cases like Planned Parenthood v. Casey in 1992 modifying the framework established by Roe. Casey introduced the “undue burden” standard, which allowed states to place restrictions on abortion as long as they did not place an “undue burden on a woman seeking an abortion.” This case opened the door for states to enact a variety of restrictions, such as mandatory waiting periods, parental consent laws, and counseling requirements.

The Overturning of Roe v. Wade
The legal landscape changed dramatically with the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization in 2022, which overturned Roe v. Wade. This decision returned the authority to regulate abortion back to individual states, leading to a significant divergence in abortion laws across the country.
The Dobbs decision has created a complex and often confusing legal environment for abortion rights in the United States. In the post-Roe era, states now have the power to regulate or ban abortion without the constraints that Roe once imposed. This has resulted in a patchwork of laws, with some states enacting strict bans, others protecting the right to abortion, and many falling somewhere in between.
Today, the primary battleground for abortion rights has shifted to the state level, where lawmakers and courts are grappling with the new legal landscape.
But keep in mind, the battle over abortion rights is still being fought. Even in states that trying to limit abortion rights, voter referendums have affirmed majority support for women’s right to choose. And it is likely that legal challenges to state laws will continue to make their way to the Supreme Court. Then again, the outcome of the 2024 Presidential and Congressional Elections could pave the way for a restoration of reproductive rights… or the opposite.
But remember, as long as there are states where abortion is legal, abortion remains an option to you. You just may be required to travel out of your own state. We’ll provide more information about that later.
State-by-State Breakdown of Abortion Law
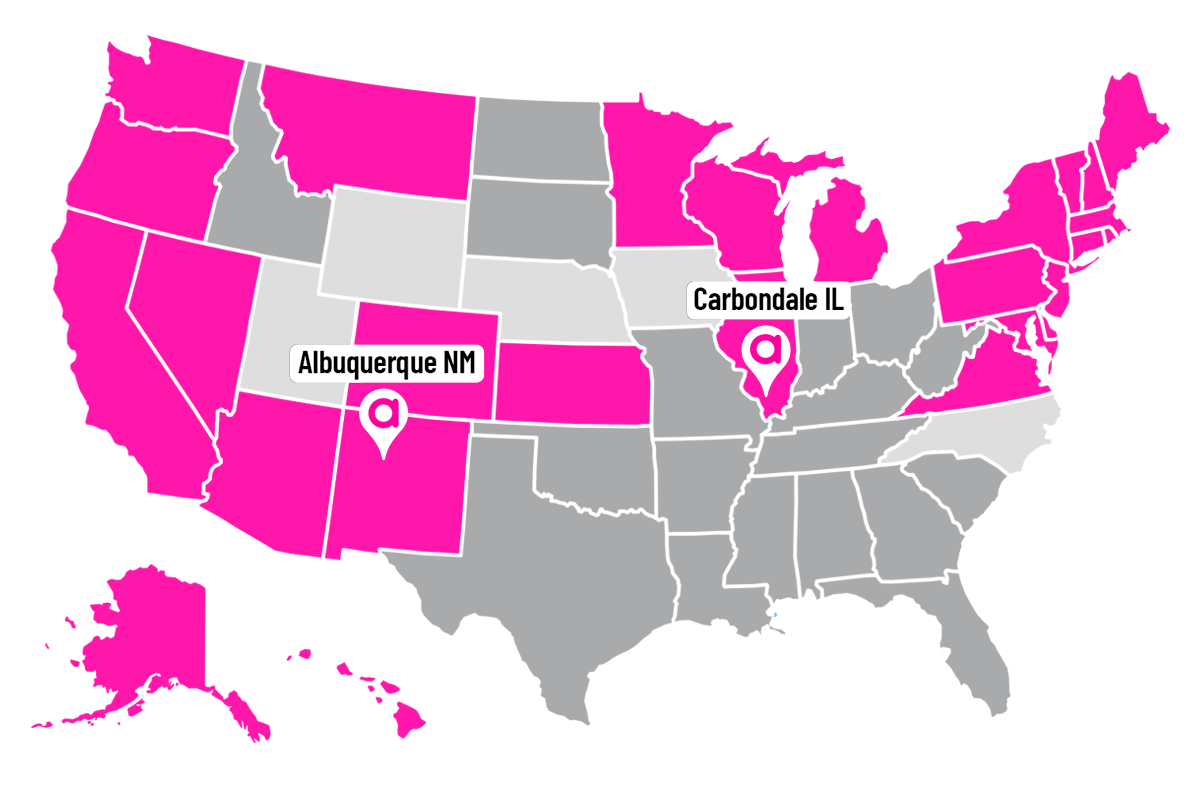
The legal status of abortion now varies dramatically depending on where you live in the United States. Some states have moved quickly to protect the right to abortion, while others have enacted bans or severe restrictions. In this section, we’ll break down the different approaches taken by states across the country.
Please keep in mind that abortion law is still undergoing changes in many states. For an up-to-date view of abortion law for your state, we recommend the following two resources:
The Center for Reproductive Rights >
AbortionFinder.org >
States Where
Abortion is Legal
In the wake of the Dobbs decision, several states have taken steps to preserve the right to abortion in state law. These states provide legal protections for women seeking abortions and for healthcare providers who perform them.
California: California has one of the most protective legal environments for abortion. The state constitution explicitly protects the right to privacy, which includes the right to abortion. Additionally, the state has enacted laws that protect access to abortion services, including for minors and individuals from out of state.
New York: New York has also solidified its commitment to protecting abortion rights. In 2019, the state passed the Reproductive Health Act, which codified the right to abortion and removed abortion from the state’s criminal code. This act ensures that abortion is available up to 24 weeks of pregnancy and beyond in cases where the mother’s life is at risk or the fetus is not viable.
Illinois: Illinois has taken significant steps to protect abortion rights, including passing the Reproductive Health Act in 2019, which guarantees access to abortion services as a fundamental right. The state also requires private insurance plans to cover abortion services, making it easier for women to access care.
These states, along with others like Oregon, Washington, and New Jersey, have created a legal environment where abortion is not only legal but protected against future federal restrictions.
States with
Abortion Bans
On the opposite end of the spectrum, some states have moved quickly to ban or severely restrict abortion following the Dobbs decision. Many of these states had “trigger laws” that were designed to take effect automatically or quickly upon the overturning of Roe v. Wade.
Texas: Texas has been at the forefront of enacting restrictive abortion laws. The state’s “heartbeat” law, SB8, bans abortions as early as six weeks, before many women even know they are pregnant. The law also empowers private citizens to sue anyone who performs an abortion or “aids and abets” the procedure, creating significant legal risks for healthcare providers and those assisting women in seeking abortions.
Alabama: Alabama’s abortion law is one of the strictest in the country. The state passed a near-total abortion ban in 2019, which only allows abortions if the mother’s life is in danger or if the fetus has a lethal anomaly. There are no exceptions for cases of rape or incest.
Mississippi: Mississippi’s 15-week abortion ban was at the center of the Dobbs case that ultimately overturned Roe v. Wade. The state now enforces this ban and has a trigger law that bans almost all abortions, with limited exceptions for rape and the life of the mother.
These states, along with others like Missouri, Arkansas, and Kentucky, have created an environment where abortion access is severely restricted or outright banned.
States with Mixed
Abortion Laws
In some states, the legal status of abortion remains unclear or is in a state of flux. These states may have conflicting laws, ongoing legal challenges, or pending legislation that could significantly impact abortion access.
Wisconsin: Wisconsin has a pre-Roe abortion ban on the books, which theoretically makes abortion illegal in the state. However, there is ongoing legal uncertainty about whether this law can be enforced, and the state’s Democratic governor and attorney general have pledged not to enforce it. The situation remains fluid as courts and lawmakers grapple with the implications of the Dobbs decision.
Michigan: Michigan is another state where abortion law is in flux. The state has a pre-Roe ban that could potentially be enforced, but the governor and other officials are working to keep abortion legal in the state. Legal challenges and ballot initiatives are expected to play a crucial role in determining the future of abortion rights in Michigan.
Arizona: Arizona’s abortion laws are currently a patchwork of restrictions and allowances. The state has a 15-week abortion ban, but there is ongoing litigation and uncertainty regarding older laws that could potentially further restrict access to abortion. The legal situation is likely to evolve as courts issue rulings on these conflicting laws.
In these states, women seeking abortions may face significant uncertainty and challenges, as the legal environment continues to evolve. It is important for individuals in these states to stay informed about the latest developments and seek legal advice if needed.
Your Rights and Access to Legal Abortion Services
Knowing your rights is crucial when navigating the complex and often confusing landscape of abortion law. In this section, we’ll explore what your rights are, how to access abortion services, and how to advocate for yourself and others in this challenging environment.
Understanding Your Rights
Your right to access abortion services depends largely on where you live, but there are some federal protections and overarching principles that apply across the United States.
Right to Privacy: The right to privacy, which was the basis for the Roe v. Wade decision, remains a key legal principle, even though Roe has been overturned. This right to privacy extends to your medical decisions, including the decision to have an abortion. However, how this right is interpreted and enforced varies by state.
Right to Travel: Even if abortion is restricted or banned in your state, you generally have the right to travel to another state where abortion is legal. This right is currently protected by federal law, although there are ongoing legal debates about whether states can restrict this right in the context of abortion.
Parental Consent and Notification Laws: Many states have laws requiring parental consent or notification for minors seeking an abortion. It’s important to understand the specific requirements in your state and what options are available if you are unable or unwilling to involve a parent.
Conscience and Refusal Clauses: Some states have laws that allow healthcare providers to refuse to perform abortions based on moral or religious objections. These laws can impact your access to services, especially in areas with few providers. Understanding your options in these situations is essential.
Accessing Abortion Services
Accessing abortion services can be challenging, particularly in states with restrictive laws. However, there are still legal and safe ways to obtain an abortion, even in difficult circumstances.
Finding a Provider:
In states where abortion is legal, you can usually find providers through online directories, health clinics, or by contacting organizations like Planned Parenthood.
In states with restrictions, you may need to travel to a neighboring state or seek assistance from organizations that help women access out-of-state services.
Telemedicine and Mail-Order Abortion Pills: Telemedicine has become an increasingly important option for accessing abortion services, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. In states where it is legal, you can consult with a healthcare provider online and receive abortion pills by mail. This option is generally available for early abortions up to 11 weeks 6 days and can be a safe and effective method.
Support Services and Organizations: Numerous organizations provide support for women seeking abortions, including financial assistance, travel logistics, and emotional support. Organizations like the National Network of Abortion Funds (NNAF) and the Abortion Care Network can help you navigate the process and access the care you need.
On our website, Alamo Womens Clinic provides a directory of organizations that can provide you with funding to help cover abortion costs.
Your Rights to Protest
In addition to knowing your rights related to accessing abortion services, it’s important to understand your rights to protest and advocate for abortion rights.
Right to Protest: The First Amendment protects your right to peacefully protest and express your views on abortion. This includes participating in demonstrations, writing op-eds, and engaging in online activism. However, it’s important to be aware of local laws and regulations regarding protests, especially near healthcare facilities.
How to Get Involved: There are many ways to get involved in the fight for abortion rights, from volunteering with advocacy organizations to participating in local and national campaigns. Whether you choose to focus on legal advocacy, public education, or direct action, your voice can make a difference in protecting and expanding abortion rights.

Navigating Challenges and Knowing Your Abortion Support Options
Seeking an abortion can be a challenging experience, especially in a legal landscape that is constantly changing. In this section, we’ll discuss some of the challenges you may face and the support options available to help you navigate this difficult time.
Financial Support
The cost of an abortion can be a significant barrier for many women, especially those with limited financial resources. In fact, it’s the number one concern for most of the thousands of women we talk to.
Cost of Abortion Services: The cost of an abortion can vary widely depending on where you live, the stage of pregnancy, and the type of procedure. It’s important to research the costs in your area and to be aware of any additional expenses, such as travel or lodging if you need to go out of state. Be sure that you are dealing only with reputable abortion clinics that honestly provide all costs upfront so you do not face any unexpected and expensive surprises.
Accessing Financial Aid: There are numerous organizations that provide financial assistance for women seeking abortions. The National Network of Abortion Funds (NNAF) is a key resource for finding financial support. Additionally, some clinics offer sliding scale fees or payment plans based on your ability to pay. Alamo Womens Clinic can help direct you to organizations that can help cover the costs of abortion procedures or travel. Contact us at toll-free at 1-800-821-7237 or check out our list of resources at alamowomensclinic.com/costs-and-funding/
Legal Challenges
The changing legal landscape has created numerous challenges for women seeking abortions, particularly in states with restrictive laws.
Anti-Abortion Laws and Prosecution Risks: In some states, women and healthcare providers face the risk of legal prosecution for seeking or providing abortions. It’s important to understand the laws in your state so that you can avoid potential prosecution. Organizations like the ACLU and the Center for Reproductive Rights offer legal support and resources.
Strategies for Legal Protection: If you live in a state with restrictive abortion laws, there are strategies you can use to protect yourself. This may include traveling to another state for the procedure, seeking telemedicine services (video or phone consultations) if available, or working with advocacy groups to understand your rights. In some cases, obtaining legal counsel before seeking an abortion may be advisable.
Emotional Support
The decision to have an abortion is deeply personal and can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to have access to support during this time.
Counseling and Psychological Support: Many women benefit from counseling before and after an abortion. There are numerous organizations that offer free or low-cost counseling services, both in-person and online. These services can help you process your emotions and make the decision that is right for you.
Talking to Loved Ones: Deciding whether to share your decision with loved ones can be difficult. If you choose to do so, it’s important to have open and honest conversations about your feelings and your reasons for seeking an abortion. Support from friends and family can be invaluable during this time.
Know Your Rights!
The legal landscape of abortion in the United States is more complex than ever, and understanding your rights is necessary to safely navigate this challenging environment. Whether you live in a state with strong legal protections for abortion or one where access is severely restricted, it’s important to stay informed and know your options.
This guide has provided an overview of the current state of abortion law, your rights, and the support options available to you. By staying informed and engaged, you can make empowered decisions about your reproductive health and advocate for the rights of all women.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. There are numerous resources and organizations ready to support you, whether you need legal advice, emotional support, or financial assistance. Stay strong, stay informed, and continue to fight for your rights.
And if you have any questions, we welcome you to call us toll-free at Alamo Womens Clinic at 1-800-821-7237. We’re here to help!


